1:理解题意:
给定一个 N×N 的区域,并且这个区域内有两类点,J 类与 B 类。现在让你在区域中添加一个J类点(也可以不添加,并且添加时不能添加到已经存在 B 类点的地方),然后找出最大的由 J 类点构成的正方形。
2:分析
2.1:概括
因为数据较小 (N<100),并且我们可以通过一条J边来确定正方形的剩下两条边,所以可以尝试通过枚举J边,并且加以判断的方法找到最大的正方形。
2.2:一点点数学
假设我们通过两点 P1 和 P2 确定了一条直线,并且 P1 的纵坐标总是比 P2 高,那么我们可以画出下图:
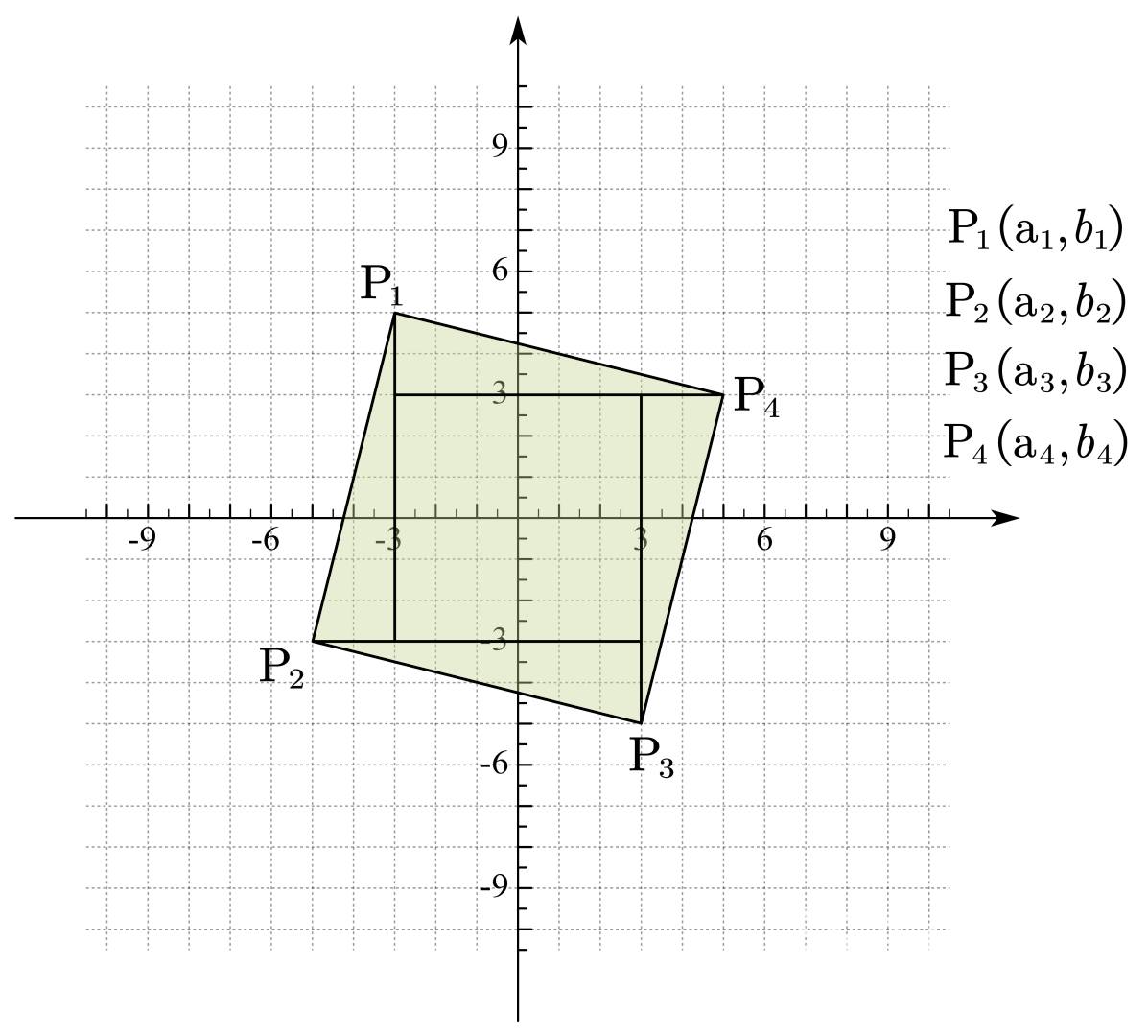
可是我们如何计算出 P3 和 P4 的坐标呢?
首先通过观察,我们可以发现图中的四个三角形都是全等的,我们只要计算出三角形的长直角边和短直角边的长度(或者说是两个不同的直角边,只是在这种特殊情况下,长边和短边的位置是图中的样式),再加上一个偏移量,就可以得到 P3 和 P4 的坐标了。
三角形的长直角边:
L△=b1−b2
三角形的短直角边:
S△=a1−a2
通过观察,我们可以从上面两个式子得出 P3 和 P4 的坐标
P3=(a2+L△,b2−S△)
P4=(a1+L△,b1−S△)
除了现在图中的样式,通过 P1P2 这条直线还能确定另一种正方形:
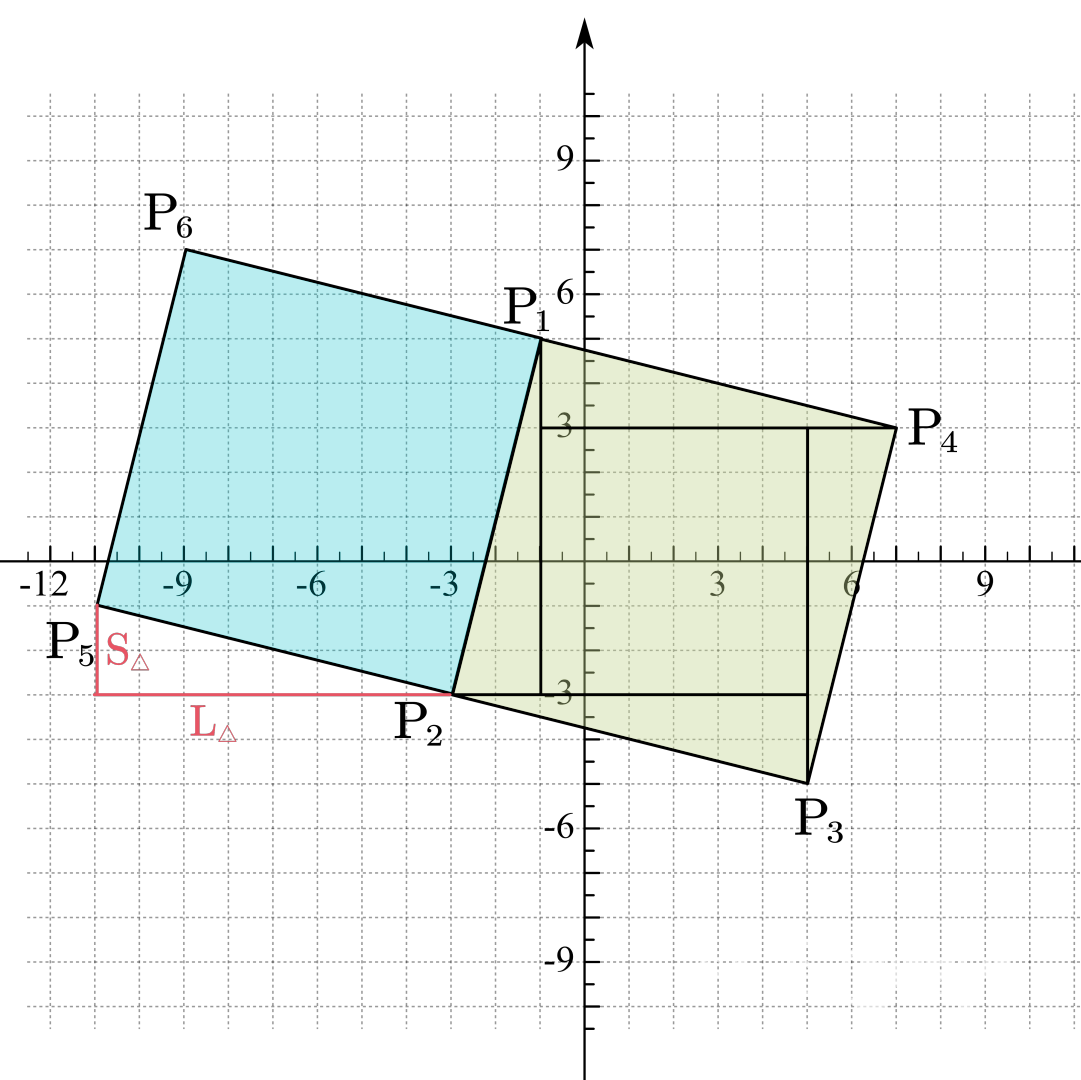
当然,我们还是可以通过刚刚的方法得到 P5 和 P6 的坐标。我们刚刚是在一个偏移量的基础上加上或是减去三角形的两个不同边的长度 (L△ 以及 S△) 来得到 P3 和 P4 的坐标,通过观察,我们可以发现只要在偏移量上进行相反的操作,就可以得到 P5 和 P6 的坐标了。
P5=(a2−L△,b2+S△)
P6=(a1−L△,b1+S△)
因为此需要我们计算的是正方形的面积,所以我们可以用以下方法计算出面积:
area=(a1−a2)2+(b1−b2)2
2.3:程序思路
通过刚刚的方法,我们已经能够得到 P3∼6 的坐标了,接下来我们需要判断通过一条边确定的这两个正方形是否合法。
因为我们可以自由的放置一个 J 点,所以整个正方形中可以只有三个现成的 J 点,当然,这一个 J 点必须放置在没有被占用的点上。
因此只要以 P1∼4 组成的正方形符合:
(P3∈JANDP4∈/B) OR (P3∈/BANDP4∈J)
注:J 表示的是 J 类点的集合,B 表示的是 B 类点的集合
我们就可以说这一个正方形是合法的。由 P1,2,5,6 组成的正方形同理
3:程序实现以及程序的改进过程
3.1:第一次尝试
想到思路之后迅速的打出了代码,结果两个点 T 了。。。
提交
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int mp[120][120];
#define debug false
struct node
{
int x, y;
};
vector<node> jc;
int n;
void input()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
char temps[110];
scanf("%s", temps);
for (int j = 0; temps[j]; j++)
{
if (temps[j] == 'J')
{
mp[i][j] = 1;
jc.push_back(node{i, j});
}
else if (temps[j] == 'B')
{
mp[i][j] = -1;
}
else if (temps[j] == '*')
{
mp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
input();
int ans = 0;
for (auto t1 : jc)
{
for (auto t2 : jc)
{
if (t1.x == t2.x && t1.y == t2.y)
{
continue;
}
if (debug)
printf("1x %d 1y %d 2x %d 2y %d\n", t1.x, t1.y, t2.x, t2.y);
node p3, p4;
node p1 = t1, p2 = t2;
if (p1.y < p2.y)
{
swap(p1, p2);
}
p3.x = (p2.x + (p1.y - p2.y));
p3.y = (p2.y - (p1.x - p2.x));
p4.x = (p1.x + (p1.y - p2.y));
p4.y = (p1.y - (p1.x - p2.x));
if (debug)
printf("3x %d 3y %d 4x %d 4y %d\n", p3.x, p3.y, p4.x, p4.y);
if (p3.x >= 0 && p3.y >= 0 && p4.x >= 0 && p4.y >= 0 && p3.x < n && p3.y < n && p4.x < n && p4.y < n)
{
if ((mp[p3.x][p3.y] == 1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] != -1) || (mp[p3.x][p3.y] != -1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] == 1))
{
ans = max(ans, ((p1.y - t2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y) + (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x)));
}
}
p3.x = (p2.x - (p1.y - p2.y));
p3.y = (p2.y + (p1.x - p2.x));
p4.x = (p1.x - (p1.y - p2.y));
p4.y = (p1.y + (p1.x - p2.x));
if (p3.x >= 0 && p3.y >= 0 && p4.x >= 0 && p4.y >= 0 && p3.x < n && p3.y < n && p4.x < n && p4.y < n)
{
if ((mp[p3.x][p3.y] == 1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] != -1) || (mp[p3.x][p3.y] != -1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] == 1))
{
ans = max(ans, ((p1.y - t2.y) * (p1.y - t2.y) + (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x)));
}
}
}
}
printf("%d", ans);
system("pause");
}
|
3.2:第二次尝试
我们可以发现这个代码做了大量的无用计算,因为我们假设了 P1 的纵坐标总是比 P2 高,所以在程序中通过一个判断来确保我们的假设成立。
1
2
3
4
| if (p1.y < p2.y)
{
swap(p1, p2);
}
|
我们实现枚举边的方法是用两个循环枚举所有的J点,所以会有重复枚举的情况(比如 P1 和 P2 实际相同,但是换了个顺序)。对于这样的情况,我们完全可以直接跳过这次循环来节省时间。
所以我们可以把代码改为:
1
2
3
4
| if ((p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y) || (p1.y < p2.y))
{
continue;
}
|
这样进入后续判断正方形合法性环节的点就都符合我们的假设了,也减少了之前的重复计算。
再仔细分析程序,我们可以发现,其实在循环内部只是做了判断正方形合法性的工作,如果在枚举的时候我们发现一个正方形的面积比我们目前得到的答案还要小,那么就没必要继续判断合法性了,直接跳过就可以了。
所以我们可以把代码改为:
1
2
3
4
| if ((p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y) || (p1.y < p2.y) || (((p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y) + (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x)) <= ans))
{
continue;
}
|
经过这次改进,我们就可以愉快的 AC 了:
AC提交记录
完整代码以及注释如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int mp[120][120];
#define debug false
struct node
{
int x, y;
};
vector<node> jc;
int n;
void input()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
char temps[110];
scanf("%s", temps);
for (int j = 0; temps[j]; j++)
{
if (temps[j] == 'J')
{
mp[i][j] = 1;
jc.push_back(node{i, j});
}
else if (temps[j] == 'B')
{
mp[i][j] = -1;
}
else if (temps[j] == '*')
{
mp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
input();
int ans = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for (auto p1 : jc)
{
for (auto p2 : jc)
{
if ((p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y) || (p1.y < p2.y) || (((p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y) + (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x)) <= ans))
{
continue;
}
cnt++;
if (debug)
printf("1x %d 1y %d 2x %d 2y %d\n", p1.x, p1.y, p2.x, p2.y);
node p3;
p3.x = (p2.x + (p1.y - p2.y));
p3.y = (p2.y - (p1.x - p2.x));
node p4;
p4.x = (p1.x + (p1.y - p2.y));
p4.y = (p1.y - (p1.x - p2.x));
if (debug)
printf("3x %d 3y %d 4x %d 4y %d\n", p3.x, p3.y, p4.x, p4.y);
if (p3.x >= 0 && p3.y >= 0 && p4.x >= 0 && p4.y >= 0 && p3.x < n && p3.y < n && p4.x < n && p4.y < n)
{
if ((mp[p3.x][p3.y] == 1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] != -1) || (mp[p3.x][p3.y] != -1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] == 1))
{
ans = max(ans, (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y) + (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x));
}
}
p3.x = (p2.x - (p1.y - p2.y));
p3.y = (p2.y + (p1.x - p2.x));
p4.x = (p1.x - (p1.y - p2.y));
p4.y = (p1.y + (p1.x - p2.x));
if (p3.x >= 0 && p3.y >= 0 && p4.x >= 0 && p4.y >= 0 && p3.x < n && p3.y < n && p4.x < n && p4.y < n)
{
if ((mp[p3.x][p3.y] == 1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] != -1) || (mp[p3.x][p3.y] != -1 && mp[p4.x][p4.y] == 1))
{
ans = max(ans, (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y) + (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x));
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
if (debug)
printf("%d", cnt);
system("pause");
}
|






![[Stanford CS144] Lab4 实验记录](/img/CS144/tcp%E7%8A%B6%E6%80%81%E6%B5%81%E8%BD%AC%E5%9B%BE.jpg)
![[Stanford CS144] Lab0-Lab3 实验记录](/img/CS144/sponge%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84%E5%9B%BE.svg)